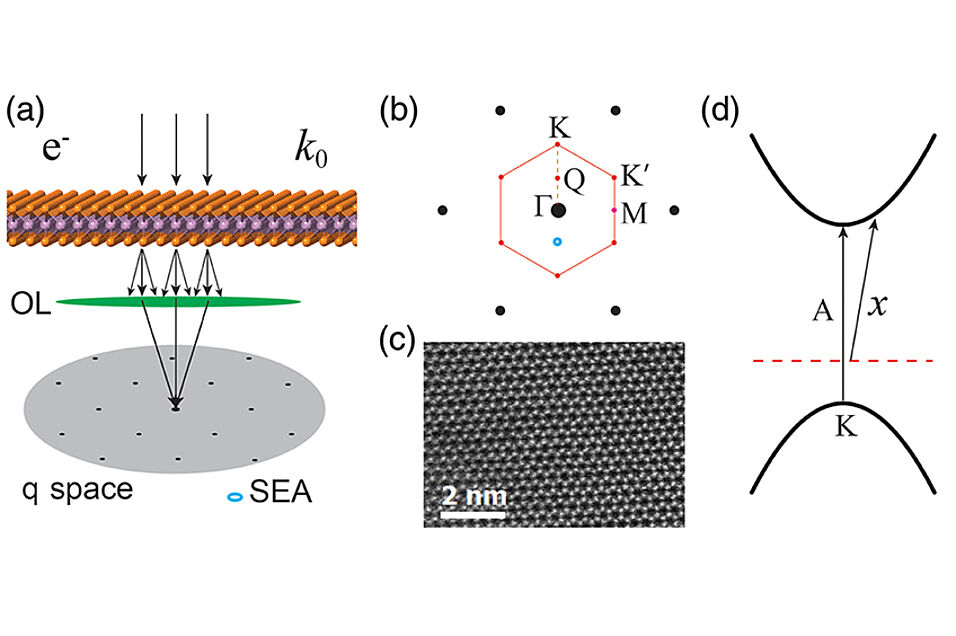
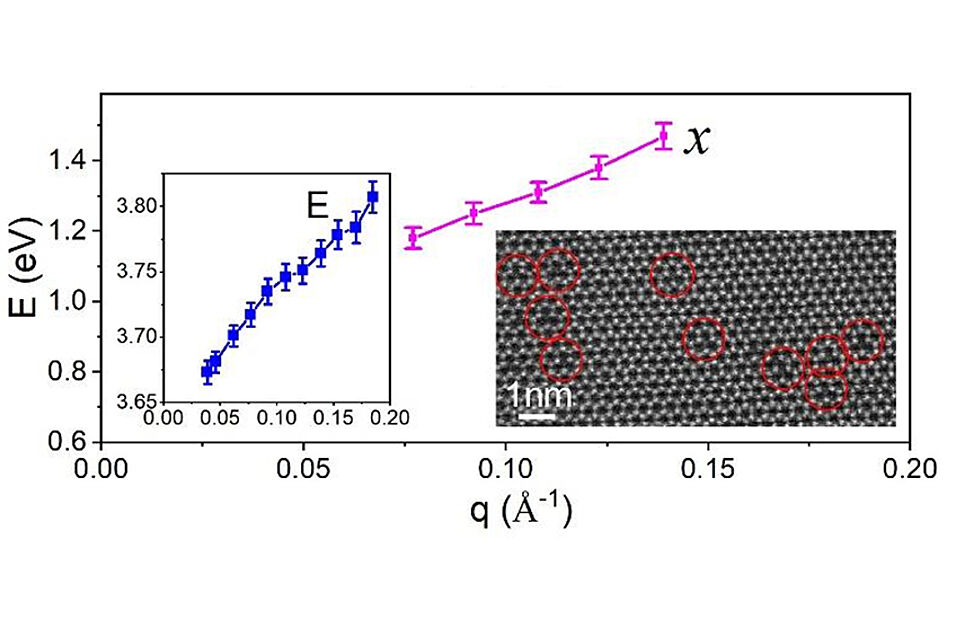
This first ever determination of the local exciton dispersion of a monolayer with nm resolution regarding Se vacancies highlights the new possibilities of TEM-EELS enabling studies of exciton dispersion and localized defect excitons at the nanoscale and down to individual monolayers without substrate interactions. This is not possible by any other complementary technique and paves the way to a completely new characterization of nanoscale properties in low dimensional materials allowing to disentangle defect excitons (x-excitons) from the normal excitons in extended 2D monolayers (examples are shown in the figure below).
Original publication in "Physical Review Letters":
Jinhua Hong, Ryosuke Senga, Thomas Pichler, and Kazu Suenaga
PHYSICAL REVIEW LETTERS 124, 087401 (2020)
DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.124.087401